You type “best pizza near me” into Google. Within half a second, you see a list of restaurants, complete with ratings, photos, and directions. Feels like magic, right?
But here’s what actually happened: Google didn’t just start searching the entire internet the moment you hit enter. That would take forever. Instead, it already knew about those pizza places. It had visited their websites weeks ago, cataloged every page, analyzed the content, and ranked them based on hundreds of factors.
This process of finding, organizing, and ranking billions of web pages is how search engines work. And understanding it changes everything about how you create content, build websites, and get found online.
What Is a Search Engine?
A search engine is a software system designed to search for information on the Internet. It collects data from across the web, organizes it, and delivers the most relevant results when someone searches.
Google handles over 8.5 billion searches per day. Bing, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo, and others add billions more. But they all follow the same fundamental process: crawling, indexing, and ranking.
Think of a search engine like a massive library. But instead of you browsing shelves, a team of librarians (web crawlers) constantly visits every book in the world, reads them, creates detailed notes (index), and organizes everything so when you ask a question, they instantly know which books have your answer (ranking).
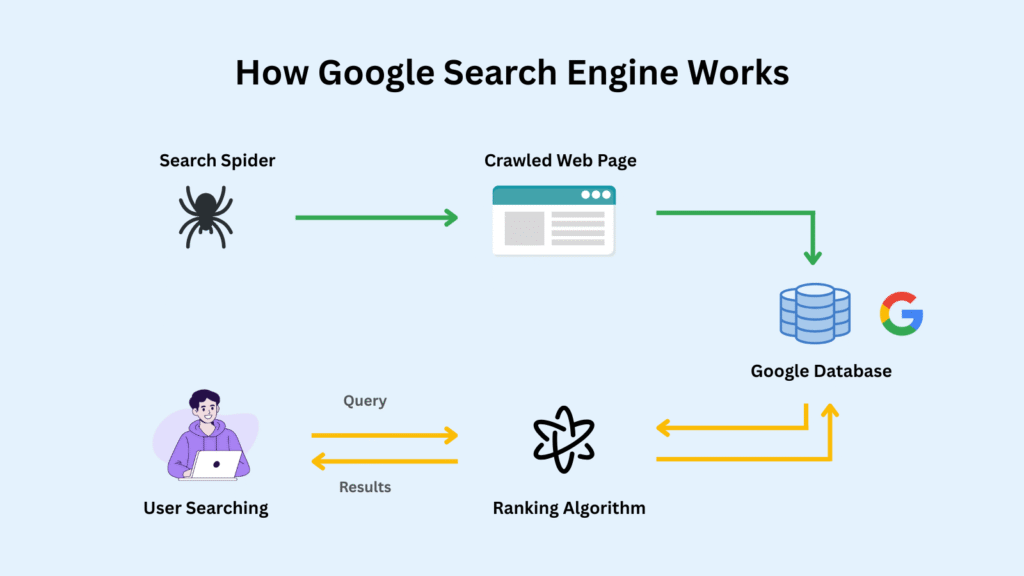
Here’s the complete picture, explained without the technical jargon. Google’s search engine runs on three fundamental processes: crawling, indexing, and ranking.
Think of it like a massive library system — Google first finds books (crawling), catalogs them (indexing), and then decides which ones are most relevant to your question (ranking). Let’s break each one down.
Stage 1: Crawling — Google’s Web Scouts
Google uses automated programs called Googlebots (also known as spiders or crawlers) to constantly explore the internet. These bots move from link to link, discovering new and updated web pages 24/7.
Here’s how crawling actually works in practice:
- Googlebots start from a list of known URLs
- They follow hyperlinks on those pages to discover new ones
- They revisit existing pages to check for updates or changes
- Pages blocked by a robots.txt file are skipped
What this means for you: If your website has broken links, poor internal linking, or is blocked by crawl settings, Google may never find your content — no matter how good it is.
Stage 2: Indexing — Google’s Filing System
Once a page is crawled, Google analyzes its content and stores it in a massive database called the Google Index. As of recent estimates, Google’s index contains over 400 billion web pages (Google, Search How-To).
During indexing, Google reads and processes:
| Element | What Google Analyzes |
| Title Tags | Main topic of the page |
| Headings (H1–H3) | Content structure and subtopics |
| Body Text | Keywords, context, and meaning |
| Images | Alt text and relevance |
| Meta Descriptions | Page summary |
| Links | Authority and credibility signals |
Google doesn’t just read keywords anymore. It understands context and intent through a system called Natural Language Processing (NLP) — powered by its BERT and MUM AI models. So when you search “best running shoes for flat feet,” Google understands you want product recommendations for a specific foot type, not a definition of flat feet.
Stage 3: Ranking — How Google Decides What Shows Up First
This is where it gets interesting. When you type a query, Google sifts through its index in under 0.5 seconds and ranks results using over 200 ranking factors. No single factor dominates — it’s a weighted combination.
The Major Ranking Factors
- Relevance: Does your page actually answer what the user is searching for? Google matches the search intent (informational, navigational, transactional) with the most relevant content available.
- Page Quality and E-E-A-T: Google evaluates content based on Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness — a framework outlined in its Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines. A medical article written by a certified doctor ranks higher than one written anonymously with no credentials.
- Backlinks: When other credible websites link to your page, Google treats it as a vote of confidence. The more quality backlinks you earn, the more authoritative your site appears.
- Page Experience: Google measures real user experience metrics called Core Web Vitals — including load speed, visual stability, and interactivity. A slow, clunky website loses ranking points regardless of content quality.
- Freshness: For time-sensitive topics like news or trending queries, newer content wins. For evergreen topics, freshness matters less than depth and authority.
Google’s Secret Weapon: RankBrain and AI
Since 2015, Google has used RankBrain — a machine learning system that helps interpret ambiguous or never-before-seen queries. It connects what you searched for with what you probably meant.
For example, if someone searches “how to stop my site from ghosting,” RankBrain understands this likely refers to crawl or indexing issues — not relationship advice.
In 2021, Google launched MUM (Multitask Unified Model), which can process text, images, and video simultaneously across 75 languages. It can answer complex, multi-part questions that previously required multiple searches.
What Happens the Moment You Hit “Search”
Here’s a quick real-time breakdown of that half-second process:
- Query Analysis — Google reads your search and identifies the intent behind it
- Index Lookup — It pulls all potentially relevant pages from its index
- Ranking Algorithm Applied — Pages are scored and ranked using 200+ signals
- Personalization Layer — Results are customized based on your location, search history, and device
- SERP Generated — The Search Engine Results Page is displayed, often including rich features like featured snippets, People Also Ask boxes, and local packs
Why This Actually Matters for You
If you’re building a business, managing a website, or creating content, knowing how Google works gives you a real competitive edge.
- Don’t write for keywords — write for people. Google has become extremely good at identifying content that genuinely helps readers vs. content stuffed with keywords to game rankings.
- Speed and mobile-friendliness aren’t optional. With Google’s mobile-first indexing, your site is evaluated based on its mobile version first.
- Authority is built over time. New websites don’t rank overnight. Earning backlinks, publishing consistent quality content, and building E-E-A-T signals takes months — but it compounds powerfully.
Final Thought
Google isn’t a mystery box — it’s a system designed to reward genuinely helpful content. The more you understand how it finds, evaluates, and ranks pages, the better positioned you are to show up where it matters. Whether you’re building a blog, launching a startup, or just curious about the internet’s backbone, this knowledge directly translates into smarter decisions online.
Start with one action: audit whether Google can even find your site using Google Search Console — it’s free, and it shows you exactly how Google sees your pages.